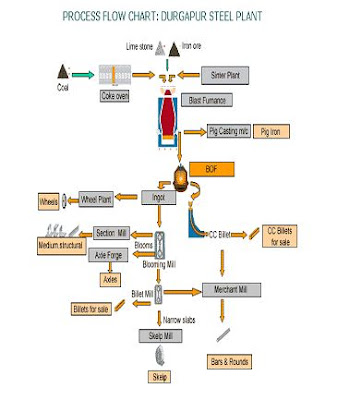
Introduction: The main function of Blast Furnace in steel industry is to produce pig iron for steel making by smelting iron ore of different grades with coke, flux and a blast of air. At present in DSP there are four Blast Furnaces of which the details are as following:-
Furnace No. Name Useful Volume Capacity Blast Temperature
1. Kasturba 1323 cu m. 1250 T/Day 11000C
2. Kamala 1400 cu m. 1870 T/Day 11000C
3. Sharada 1400 cu m. 1820 T/Day 11000C
4. Durga 1800 cu m. 2340 T/Day 12000C
The raw materials used are:
- Coke: Hard porous coke, which serves as a source of heat and a reducing agent
- Flux(limestone & dolomite): Flux is used to combine with the gangue material of the ore and the ash of the coke to form a fusible mass known as slag which is used in the cement production.
- Blast of Air: A hot blast of air is given to the mass to supply necessary oxygen for combustion.
- Iron ore - Bolani, MMTC
- Limestone - Birmitrapur, Birla
- Manganese ore - Bolani, MMTC, Barabil
There is a storage house for the various raw materials used for the charging the blast furnace. Iron ore, coke, flux, Manganese ore, quartzite etc are stored in the bunkers. These bunkers are fed by conveyers and also by wagons. Scale cars running below the bunkers on track charged the required amount of raw materials into the skips and skips charge them into the blast furnace. The scale car is not being used in blast furnace II.
The raw materials are charged into the furnace from the top in the required proportion and then preheated air is blown in through a number of symmetrically placed openings called tueyers. The main air pipe is known as Bustle pipe. The reducing gases rise up through the descending raw materials. The descending raw materials travelling through the various temperature zones are heated up, prepared and gets smelted. The liquid iron and the liquid slag formed trickle and accumulate in the hearth, which is the bottom most part of the blast furnace. The slag separates and floats above the liquid metal, as it is lighter than the hot metal. The descending raw materials takes 10-12 hours to descend and gets melted, whereas the gases take only a few seconds to ascend. The slag produced is separated from the molten metal with the help of an obstruction, which is known as skimmer and is boat shaped, is poured into ladles, which are then sold or sent to Durgapur Cement Works for cement production.
TYPICAL ANALYSIS OF THE BLAST FURNACE PRODUCTS
Hot Metal: Si=1.67% S=0.45% Mn=0.46% Slag: SiO2=32.9% Al2O3=23.5% MgO=4.2% CaO=35.9% Blast Furnace Gas: CO2=14.4% O2=0.2% CO=25.8% H2=2.8%